Lion’s mission is to earn the confidence and satisfaction of customers by providing excellent products and services that make a difference in everyday lives by redesigning habits.
Based on our Quality Policy, we create high-quality products that meet customer needs.
In 2018, we established the Reliability Assurance Department to reinforce quality assurance based on a Product Management System covering the entire supply chain.
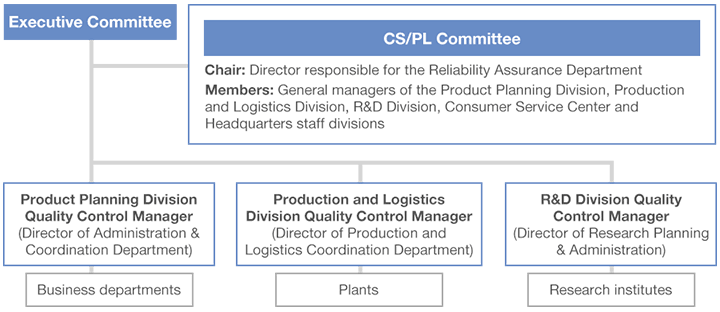
To implement quality assurance activities on a Company-wide basis, we have established the CS/PL Committee,* comprising representatives of the Product Planning Division, Production Division, R&D Division, Consumer Service Center and headquarters staff divisions. The Reliability Assurance Department serves as the secretariat for this committee. The CS/PL Committee provides overall management of quality assurance activities, monitoring Group-wide efforts and responses to issues in the areas of legal compliance, setting voluntary standards and targets, and developing superior products from the perspective of reliability assurance. Lion manufactures and sells products ranging from everyday sundries to pharmaceuticals, so its quality assurance system is designed in line with the respective standards for each product category.
Furthermore, Lion maintains a system for swiftly taking the necessary measures to address any serious problems that may arise with its products. These measures include responding to individuals harmed or affected, disclosing relevant information to government authorities and customers, issuing product recalls and taking steps to prevent recurrences.
* CS/PL Committee: A committee focused on customer satisfaction (CS) and product liability (PL)
Based on its Quality Policy, Lion has established a Product Management System, comprising regulations stipulating work processes and quality assurance practices at each stage of product development, in order to steadily and rationally develop excellent products and services that make a difference in everyday lives by redesigning habits.
This system is compliant with ISO 9001, the international standard for quality management systems. It defines the flow and mechanisms of quality assurance processes at each step of product development (strategy, planning, development, production, sales, post-launch improvements and disposal). Through the system, we put these processes into practice. Lion’s headquarters, Sapporo office, Sendai office, Nagoya office, Osaka office, Fukuoka office, Singapore office, research centers (Hirai Research Center and Odawara Research Center) and plants (Chiba Plant, Odawara Plant, Osaka Plant and Akashi Plant), as well as six domestic affiliated companies (Lion Chemical Co., Ltd., Lion Specialty Chemicals Co., Ltd., Lion Hygiene Co., Ltd., Lion Pet Co., Ltd., Lion Engineering Co., Ltd. and Lion Dental Products Co., Ltd.) have acquired the ISO 9001 multi-site certification.
Lion’s auditing officers and staff periodically carry out quality audits of Lion and its contractors, providing guidance on improvement as needed. Locations are chosen from among all the operations of Lion and its contractors that are subject to these audits, and the selection of locations to undergo on-site surveys is informed by the timing and results of previous surveys.
The Lion Group is expanding operations across Asia in line with its mission of providing excellent products and services that make a difference in everyday lives by redesigning habits. In recent years, the volume of intercompany import and export business between overseas group companies has been expanding. At the same time, there is a growing trend toward tighter regulations internationally, increasing the importance of greater coordination among quality management staff in each country.
In light of these changes, starting in 2018, we held the first annual Asia QA* Meeting, bringing together import, export and quality management staff from overseas Group companies. This meeting was held in person at Lion Headquarters, and a site tour of the production area was conducted at the Chiba Plant. Discussions were conducted, focusing mainly on the status of operations and issues on the ground as well as the creation of a system for coordination going forward, with the aim of reinforcing the Group-wide quality assurance system.
Going forward, we will continue to implement initiatives like this, striving to provide better products and services to customers in all the countries where we do business.
* QA: Quality assurance

To ensure that customers can use Lion products with confidence, we evaluate the safety of raw materials and ingredients as well as of final products during use.
Before using a raw material, we first review existing data and information to determine its physical characteristics and if it has any hazardous properties (hazard assessment) as well as whether we will be able to safely use it in the product being developed (risk assessment). With the wide-ranging customers that use our products in mind, and with reference to safety reports from international organizations and standards in and outside Japan, we determine whether or not the material is suitable for use in the product.
Furthermore, in addition to health-related considerations, we similarly examine the material’s impact on the environment after its use by consumers in line with the latest scientific appraisals. Based on these comprehensive considerations, substances deemed to require caution are carefully listed and managed.
When existing data is insufficient to reach a determination, we perform safety tests using officially designated and other objective methods of evaluation. Through such testing, we determine the limits within which the raw material can be used safely, taking into account the way the product will be used. Finally, for raw materials deemed suitable for use, we establish standards based on their applications (such as use in pharmaceuticals, quasi-drugs, cosmetics, food products or sundries). Raw materials that meet these standards are used in product manufacturing.
As with the raw materials of the product contents, we use only materials that meet appropriate standards for product packaging and containers.
Even after products are launched, we continue to analyze research data on the raw materials and ingredients used to confirm that there are no issues with their continued use.
In some cases, small amounts of impurities arising from raw materials or manufacturing processes end up in products. Even if such impurities present no health concern, Lion implements quality management at every stage, including raw material purchasing and production, to reduce impurities as much as is feasible. One example of such efforts is Lion’s response to a notice published by the Japanese government in 2012 about organic pigments that could have been unintentionally contaminated with polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs). Upon the notice’s publication, Lion moved quickly to confirm that there were no safety issues with its products. Since then, in accordance with the government’s guidance, Lion has purchased and used such raw materials produced using designated best available technologies (BATs). Through efforts like these, we ensure that any impurities in our products are maintained at low levels that are safe for customers and the environment.
Giving due consideration to the various ways products may be used as well as product use by socially vulnerable customers, we perform safety evaluations based on an approach of avoiding risks at the product design stage.
To this end, we use a checklist to determine whether the product design ensures safety in both “normal use” and “mistaken use” cases. For “irregular use” cases, we assess whether risk reduction is possible and whether the risk is tolerable, and as necessary clearly label the product with an explicit safety warning.
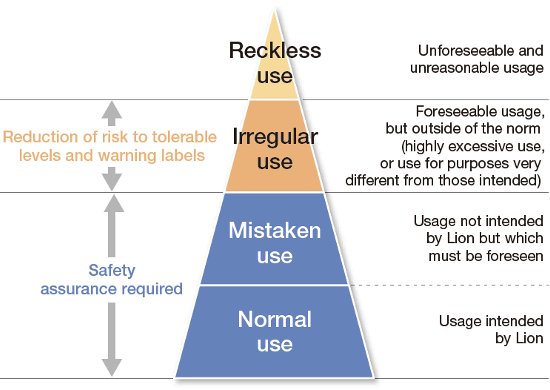
In addition, the quality verification meeting, which encompasses representatives of related departments, performs assessments based on customer use scenarios in order to prevent harm related to product use and to prevent the omission of items that should be checked for safety.
If there is trouble with a product, we have an internal system in place, ready to promptly issue product recalls or otherwise respond as needed.
Businesses must swiftly collect and centrally manage information from customers about the bodily issues they experience and quickly respond as appropriate.
Information on bodily issues from customers who have used Lion products is collected and centrally managed by the Consumer Service Center. We have in place a framework for quickly and appropriately responding to such information, including sharing the information received with multiple specialized departments and reporting it to top management.
Going forward, we will continue to educate staff involved in implementing responses about the importance of centralized data management and to collect and manage such information.
In accordance with the Lion Group Charter for Corporate Behavior and Behavioral Guidelines Lion complies with the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Act, Act against Unjustifiable Premiums and Misleading Representations, Health Promotion Act and other related laws and regulations. Furthermore, Lion strives to consider customer perspectives in order to make accurate and reasonable product representations (such as labels and advertising) that will not lead to misunderstandings or negative customer experiences.
To improve the quality of representations about all the products it sells (including food and pharmaceutical products), Lion has clearly defined its basic approach to product representation and established a representation drafting manual, comprising guidelines for preparing precise, appropriate product representations at each step of product development under its Product Management System. These guidelines apply to all product packaging and presentation as well as the wording and expressions used in instructions, pamphlets, sales handbooks, advertisements and other representations (including those for samples).
In line with the guidelines for product representations, representations are subject to stringent checks by specialized staff as well as external experts (attorneys, etc.), as needed. Through this system of thorough management, we advance the use of representations that are clear and easily recognizable to customers.
Lion’s specialized representation checking staff strive to improve their expert abilities to ensure that they can make decisions and offer advice about representation quality that accurately reflect the latest legal interpretations, governmental tendencies and changes in society. To this end, they participate in lectures offered by governmental bodies and external seminars and, as needed, consult with external experts and governmental authorities.
The information displayed on pharmaceutical product labels is subject to the stipulations of the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Act (statutory labeling). The laws and regulations regarding fairness and appropriateness in pharmaceutical product advertising include the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Act and the Standards for Proper Advertisement of Pharmaceuticals, etc., while industry self-regulations include the Japan Federation of Self-Medication Industries’ Guidelines for the Proper Advertising of Over-the- Counter Medicines.
We believe that advertisements for pharmaceutical products that protect users’ lives and health should be not only marketing information, but also information to encourage customers to use pharmaceutical products properly. Such advertisements must not encourage improper use, abuse or overuse due to insufficient caution.
Lion’s departments in charge of creating and checking product representations share pharmaceutical product information templates for statutory labeling and an advertising check sheet based on the Standards for Fair Advertising Practices concerning Pharmaceutical Products, etc., for advertisements. By ensuring that representations are created and managed based on a common understanding of the regulations stipulated in the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Act, we strive to efficiently and accurately advance proper representations.
The Japan Federation of Self-Medication Industries has established an advertising screening committee, which works toward appropriate advertising and evaluates pharmaceutical product advertisements after their publication. Comprising third-party and over-the-counter (OTC) drug manufacturer representatives, the committee works to ensure proper expressions in OTC pharmaceutical product advertising and enhance confidence in such advertising. Lion participates as a corporate member, contributing to efforts to ensure proper OTC drug advertising.
* OTC drugs: Pharmaceutical products that can be purchased at a pharmacy or drug store without a prescription. (Source: Japan Self-Medication Industry)
The contents to be labeled on food products are defined by the Food Labeling Standards under the Food Labeling Law (statutory labeling). In addition, the Act against Unjustifiable Premiums and Misleading Representations, the Health Promotion Act, and other legal regulations govern the proper labeling and advertising of health food products* handled by the Company, while the Fair Competition Code on the Labeling of Foods for Specified Health Uses and its enforcement regulations serve as fair competition codes.
Food products have three basic functions. The first and most important is nutrition (the primary function), the second is the sensory and enjoyment function (the secondary function) and the third is contributing to biological regulation to help maintain or improve health (the tertiary function). The food products that Lion sells are health food products*1 that provide this tertiary function. While these products are thought to provide a health effect, it is important to ensure that they are properly marketed to avoid such misunderstandings as their being confused with pharmaceutical products or their effects being exaggerated.
Lion uses food product information templates for statutory labeling and an advertising check sheet based on related laws and regulations and voluntary industry rules for advertising. Furthermore, to ensure the provision of appropriate information to customers, checks by external experts (attorneys, etc.) as a third-party perspective are established in the advertisement confirmation step of the process as necessary.
*1
Health Food Products
The term “health food product” generally refers to any product that is claimed to be beneficial to health. In Japan, health food products that are labeled as having certain functions based on standards of safety and effectiveness established by the national government are classified as foods with health claims. There are three types of foods with health claims: foods with function claims*2, foods for specified health*3 uses, and foods with nutrient function claims.
*2 Foods with function claims are food products that display claims of functions for which, prior to sale, manufacturers must submit scientifically based information on safety and functionality to the Director-General of the Consumer Affairs Agency. The manufacturers themselves are responsible for ensuring the accuracy of such information.
*3
Foods for specified health uses
Foods for specified health uses are food products for which permission to display claims of health functions has been granted by the Director-General of the Consumer Affairs Agency based on evaluations by the agency of the product’s safety and usefulness in maintaining or improving health.
Lion received an admonishment from the Consumer Affairs Agency under its Health Promotion Act regarding an advertisement for its product Tomato Su Seikatsu Tomato Su Inryo that ran from September 15 to November 27, 2015 in the daily newspaper on the grounds that said advertisement could be misunderstood by general consumers.
Lion takes this admonishment seriously. We have further reinforced advertisement submission management and are steadily advancing measures to prevent recurrences of such issues.
Lion’s food products, particularly its processed food products in tablet form, are easy to consume and therefore present the potential risk of excessive intake. By such means as displaying recommended intake amounts in large print on the front of packages, Lion strives to provide clear labeling so that consumers can use its health food products appropriately.
Lion requires its raw ingredient manufacturers and suppliers to provide information about their use of the eight ingredients that under the Food Labeling Standards are required to be listed on food product labels as allergens, as well as the 20 ingredients recommended for such labeling.* In particular, we carry out tests as appropriate to ensure appropriate labeling regarding functional substances (used as ingredients in foods with function claims) and substances with specified uses (used in foods for specified health uses).
Lion shares information about revisions to allergy labeling regulations and other such developments internally, mainly through a food safety team.
*
Eight raw ingredients required to be listed as allergens: eggs, milk, wheat, buckwheat, peanuts, shrimp, crab and walnuts
20 raw ingredients recommended to be listed as allergens: apples, oranges, soy, sesame, etc.
To ensure that customers can accurately understand the features of our products, our product labels, including usage instructions and ingredient lists, are presented in the official languages of the places where they are sold.



To ensure thorough compliance with laws and regulations related to product representations (the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Act, Act against Unjustifiable Premiums and Misleading Representations, Health Promotion Act, etc.), Lion provides e-learning for all employees and lectures for employees in related divisions as part of its legal education initiatives.
Every year, Lion educates employees involved in the planning and sale of pharmaceutical and related products on product safety. This education, based on the Ministerial Ordinance on Good Vigilance Practice for Drugs, Quasi-Drugs, Cosmetics, and Medical Devices (the GVP Ordinance), teaches employees about the handling and correct use of safety information. Lion uses specified procedures for education about product representations to promote proper promotional activities. The education also covers related laws and regulations and appropriate product representations.
In Japan, under the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Act, businesses must obtain a marketing license to manufacture and sell pharmaceutical products and quasi-drugs. Per this law, businesses must conduct appropriate management and supervision by establishing and properly operating systems of quality assurance and post-marketing safety control for such products and appointing a general marketing director, quality assurance director and safety control director.
As a company that manufactures and sells pharmaceutical products, quasi-drugs and cosmetics, Lion complies with such legal requirements and operates an appropriate marketing framework. Lion has created a manual for compliance with the GVP Ordinance for use in safety control. Safety control is carried out in accordance with this manual and managed by the safety control director. Furthermore, the safety control director manages the safety control divisions, and the general marketing director provides oversight to ensure proper operations and conducts post-marketing safety control. The safety control divisions operate according to internal manuals, including implementing post-marketing safety measures for the products Lion sells, collecting and evaluating safety data about pharmaceutical and other products, and, as needed, implementing safety measures.
The safety control divisions provide education and training to divisions that implement safety control to better promote the proper use of pharmaceutical and other products.
To further enhance the safety of the pharmaceutical products it sells, Lion has been a member of the Japan Self-Medication Industry, an organization of OTC drug manufacturers, since 1978. A representative from Lion serves as a vice chair of said organization. The Japan Self-Medication Industry works to provide information about the correct use of OTC drugs and examines all kinds of issues related to OTC drugs, for example, researching how to make drug package inserts easier to read and understand.
Lion’s safety control director and others regularly take part in the organization’s committee meetings to gather the latest information on safety about the Act on Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices and OTC drugs for safety control and legal compliance.
In addition to the Japan Self-Medication Industry, in the area of pharmaceutical products, Lion is a member of the Pharmaceutical Manufacturers’ Association of Tokyo, and in the areas of quasi-drugs and cosmetics, Lion participates in the activities of the Japan Dentifrice Manufacturers’ Association (JDMA) and the Japan Cosmetic Industry Association. Through such participation, Lion suggests research initiatives and measures related to regulations and conducts educational programs for customers about correct product use with the aims of promoting the manufacturing and quality control of pharmaceutical and other products as well as post-marketing safety management and correct product use.
The Lion Group adheres strictly to the international principles of the 3Rs for animal testing (Replacement, Reduction, Refinement) and supports the philosophy of animal welfare.
We proactively work to thoroughly ensure the safety and enhance the functionality of our wide range of products and services to better serve our customers. In developing cosmetics products (including medicated cosmetics), we do not use animal testing apart from exceptional circumstances in which it is required to ensure safety or satisfy legal requirements. Similarly, in developing other products, we employ alternative methods as long as the accuracy and replicability of the scientific data used as the basis for evaluating products are not negatively affected. When no alternative methods are available and we must use animal testing, we strive to do so properly and in line with the principles of the 3Rs and the laws of relevant countries.
Lion Corporation has long focused efforts on related research through participation in the Long-range Research Initiative of the Japan Chemical Industry Association and the Japanese Society for Alternatives to Animal Experiments. We will continue actively developing alternatives to animal testing and advancing business activities that contribute to both the health of our customers and animal welfare.