-
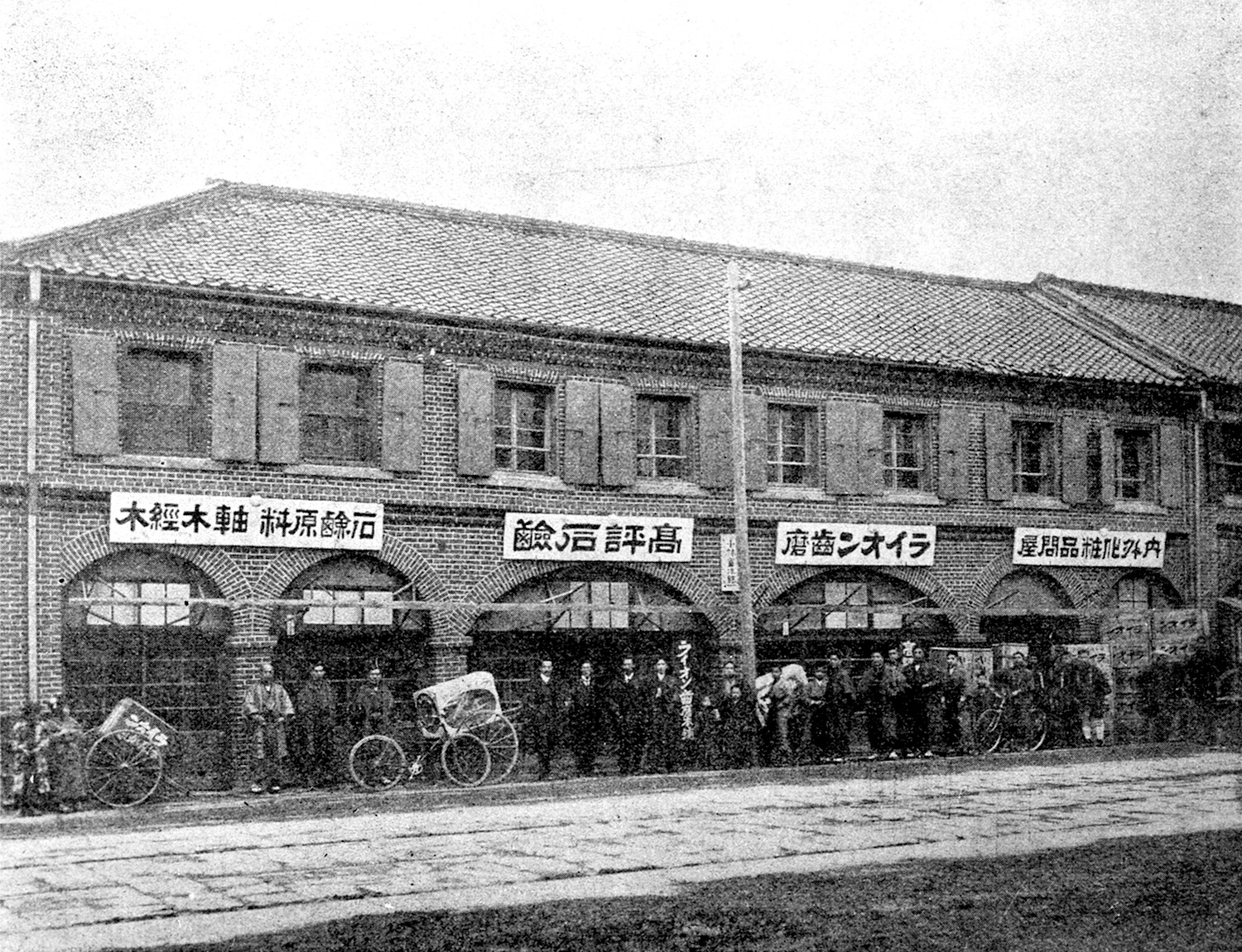
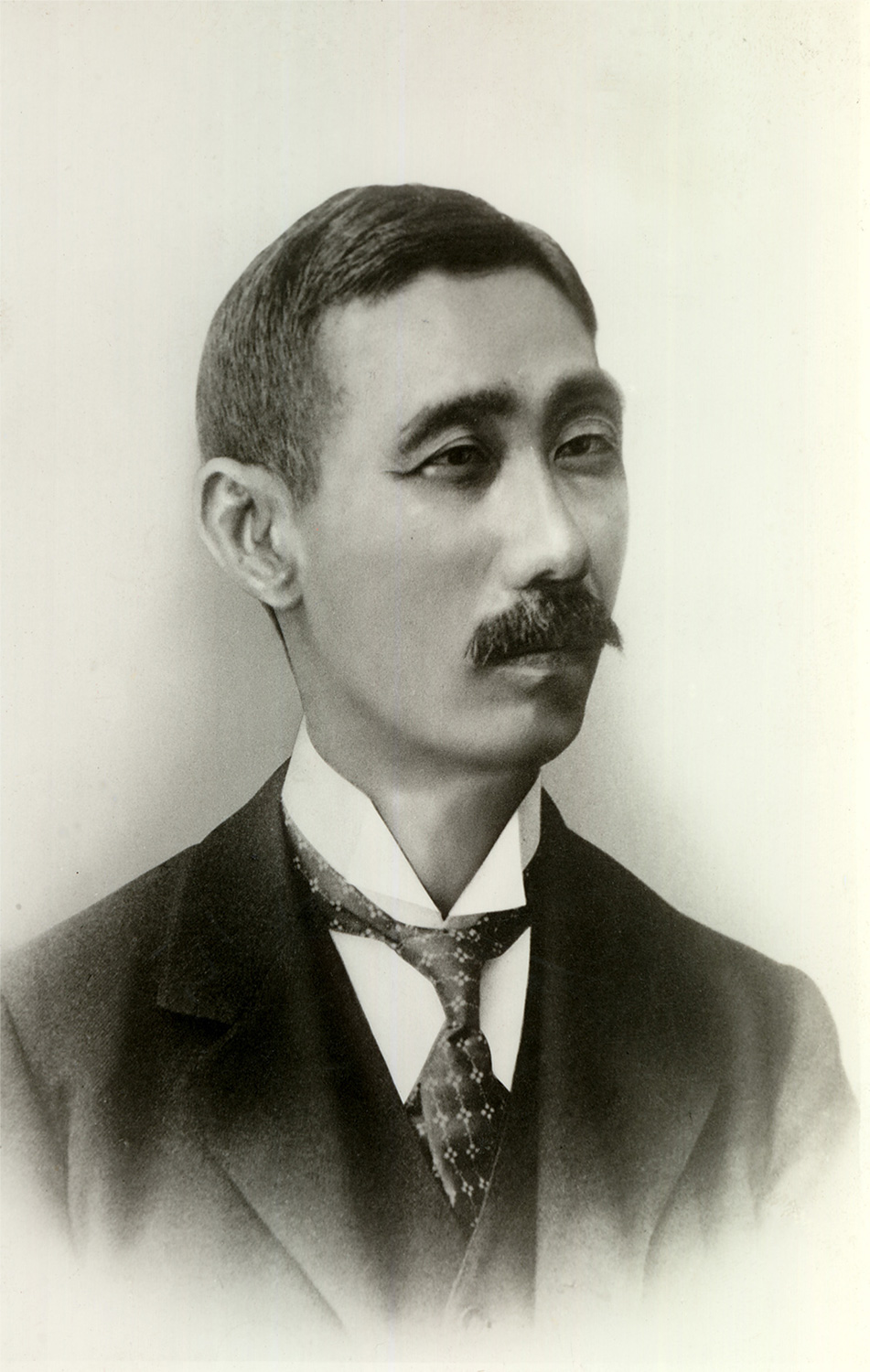
1891
The birth of Lion
Founder Tomijiro Kobayashi established T. Kobayashi & Co. on the Yanagihara riverside in Kanda, Tokyo, to trade in soap and raw materials for matches


-
1900
Lion's first social contribution initiative
Began a social contribution program using charity coupons printed on packets of Lion Toothpowder

-
1913
Japan's first toothpaste for children
Held first oral hygiene lecture
Launched Kodomo Toothpowder (today Kodomo Toothpaste) for schoolchildren
The young swordsman illustration was drawn by Nihonga artist Kiyokata Kaburaki
@Akio Nemoto 02023/JAA2300016 -
1920
Japan's first plant-derived laundry soap
Launched plant-derived Lion Laundry Soap

-
1921
Japan's first dental clinic for children
Opened a dental clinic for children (renamed the Lion Dental Clinic for Children in 1938)

-
1933
Spreading better laundry washing methods
Opened the Family Laundry Information Service Center (renamed the Lion Laundry Science Laboratories in 1936 and the Household Science Laboratories in 1957)

-
1956
Launched Lipon F, Japan's first kitchen detergent for washing fruits, vegetables and tableware. Lipon F was the first product endorsed by the Japan Food Hygiene Association.

-
1959
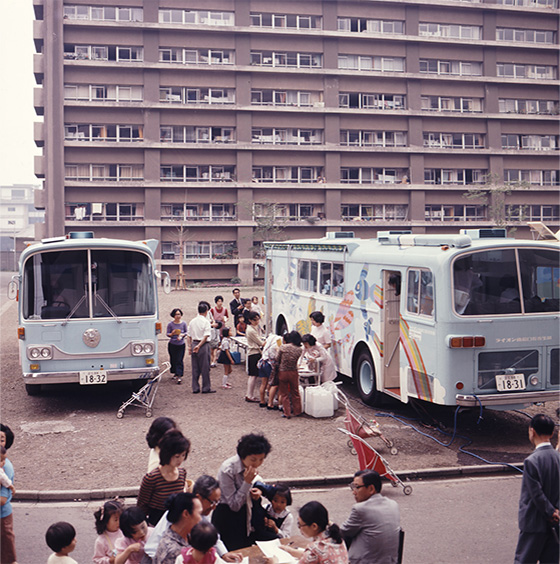
Oral Hygiene Education Activities
Developed dental hygiene activities for mothers and their children (later named the "Tanpopo Initiative")

-
1967
Detergent with an ingredient that Lion was the first in the world to successfully commercialize
Launched the laundry detergent Dash, containing alpha olefin sulfonate (AOS), a new, highly biodegradable surfactant

-
1971
Established the Environmental Problems Countermeasures Committee
-
1973
Created phosphate-free detergent, ahead of the industry
Moved ahead of the times to develop an early phospate-free detergent and released it as Seseragi

-
1980
Majorly successful phosphate-free detergent
Launched Murin Top (Enzyme Power Top), a more environmentally friendly detergent that does not sacrifice detergency

-
1989
Sustainable, carbon-neutral plant-based raw materials
Founded Lion Oleochemical Co., Ltd., which produces highly biodegradable raw surfactant materials from palm oil
-
1990
Established the Environmental Action Promotion Committee (renamed Environmental conservation committee in 2004, Sustainability Promotion meeting in 2019)
-
1991
Primary washing ingredients made from 100% palm oil-derived plant-based ingredients
Launched Spark laundry detergent, formulated with the surfactant MES, made from environmentally friendly plant-based ingredients derived from palm oil

-
1996
Received the Minister of International Trade and Industry Award as a consumer-oriented excellent company
Published the Company's first Environmental Report -
2001
All of Lion's factories received ISO 14001 certification
-
2006
ECO LION Declaration
Established the Lion Eco Standards as a set of new criteria for product environmental friendliness
Established the Lion Forest in Yamanashi -
2007
Received the 16th Grand Prize for the Global Environment Award
Successfully replaced the washing ingredients in laundry detergents with ingredients made from plant-based raw materials, reducing carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from household laundry by 47% (compared with 1990 levels)

-
2008
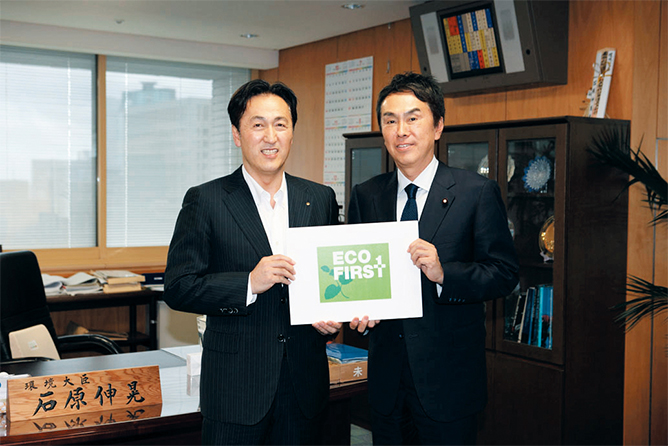
Became the first manufacturer to receive Eco-First certification from the Ministry of the Environment
Through the Ministry of the Environment’s Eco-First Program, Lion is reinforcing coordination among Eco-First Program member companies and environment-related governmental bodies while accelerating initiatives to address environmental issues

-
2009
-
2010
Released TOP NANOX super-concentrated liquid laundry detergent, formulated with plant-based high-detergency ingredient MEE for easy, one-rinse washing and environmental friendliness (this product was rereleased as TOP SUPER NANOX in 2016)

-
2013
Announced Eco Vision 2020, a set of environmental targets
-
2014
Environmental communication through products: Launched an environmental logo and environmental label for use on Lion’s environmentally friendly products
To help customers to choose environmentally friendly products, products that meet the proprietary Lion eco-standard bear our environmental label, which includes the “eco Lion” mark, the slogan “Every Day. For the Earth” and the factors that make the product environmentally friendly.
Launched LOOK Plus Awa-Pita Toilet Cleaning Spray
(Received the Japan Star Prize, the top prize in the 2022 Japan Packaging Contest)
Recertified as a member of the Eco-First Program.

-
2015
Promoted the Toothbrush Recycling Program
Launched a program in cooperation with TerraCycle LLC to collect used toothbrushes and recycle them into planters and other products. The project is ongoing, with participation from numerous municipalities, schools and other organizations.

-
2019
-
2020

-
2022
Acquired certification under the ISO 9001 international quality management standard
Adopted internal carbon pricing in domestic operations
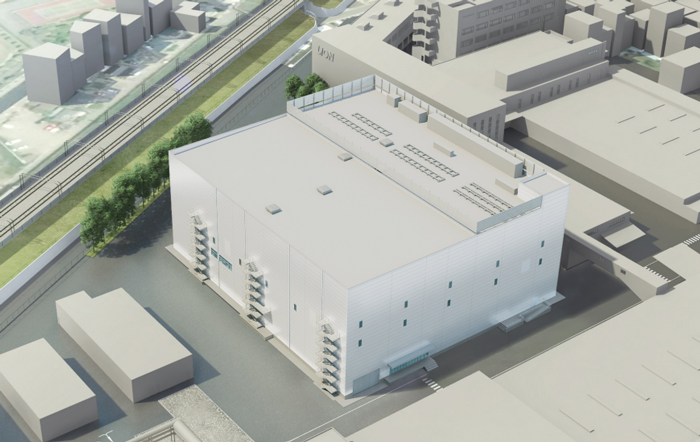
(Image is a rendering of the completed factory for over-the-counter drugs (Odawara City, Kanagawa), which will be set up in conformity with the pricing system) -
2023



Jointly received the Award of the METI Director-General for Commerce and Service Industry Policy under the Excellent Green Logistics Commendation Program.
The award was given in recognition of the collaborative efforts of several companies from different industries, including logistics companies, consignors and consignees, to improve transportation efficiency while reducing environmental impact, such as CO2 emissions, and improving the working environment for drivers.
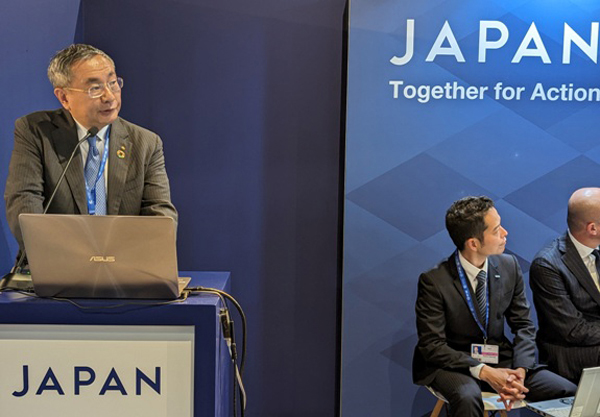
Conducted a presentation at COP28 Japan Pavilion Seminar hosted by Ministry of the Environment.
A presentation was given on the Company's efforts to realize a decarbonized society at the 28th Conference of the Parties (COP28) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change under the theme “The great potential of our lifestyles and how we can realize that potential.”

-
2024
Lion Collaborates with JICA to Strengthen Support for Hygiene Education in Bangladesh
Contributing to the development of cleanliness and hygiene habits in Bangladesh
Concluded an agreement to support the hygiene education of elementary school students and teachers, as well as parents and local residents in Bangladesh through the Japan International Cooperation Agency.
Close